Electronic Hardware for Robotics: Sensors, Motors, and Control Systems
About Course
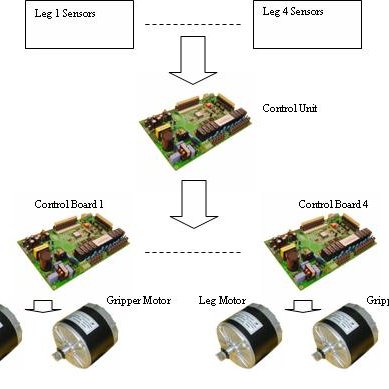
Step into the fascinating world where mechanical precision meets intelligent control! Electronic Hardware for Robotics offers a deep dive into the vital components that bring robots to life—sensors, motors, and control systems. From detecting the environment to executing precise movements and making real-time decisions, this course explains how each hardware element contributes to the seamless function of modern robots. Whether you’re building a robot for fun, automation, research, or competition, understanding the “electronic nervous system” is key.
You’ll explore various types of sensors and motors, understand how control systems like PID work, and get familiar with the brains behind it all—microcontrollers and embedded platforms. With simplified explanations and practical examples, this course will empower you with the technical foundation necessary to start designing and assembling intelligent robotic systems. It’s the perfect starting point for aspiring roboticists, engineers, or anyone who wants to master the hardware side of robotics.
Course Content
Introduction
Introduction to electronic hardware in robotics
00:00Importance of electronic hardware in robotics
00:00Purpose of the Ebook
00:00