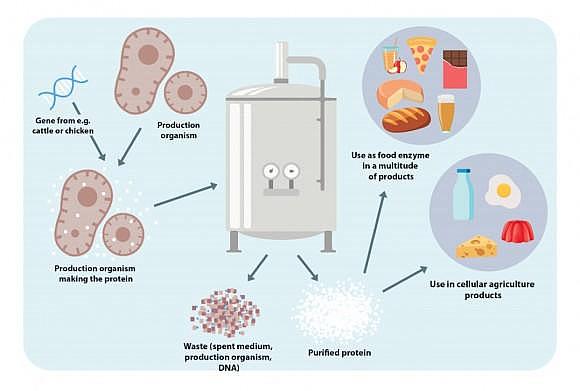
Cellular Agriculture: Transforming the Future of Sustainable Food Production
Course Content
Introduction
-
The Global Food Challenge
00:00 -
Introducing Cellular Agriculture
00:00 -
The Promise of Sustainable Food Production
00:00 -
Overview of the Ebook
00:00