Fuel Cells 101: An Introduction to the Basics of Fuel Cell Technology
About Course
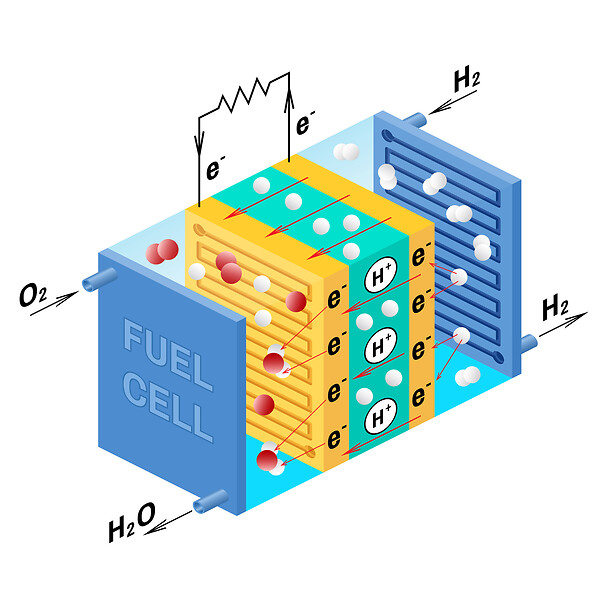
In an age where clean energy is no longer a luxury but a necessity, fuel cell technology stands out as one of the most promising solutions. This beginner-friendly course introduces you to the world of fuel cells—devices that convert chemical energy directly into electrical power with high efficiency and minimal environmental impact. From powering buses and cars to providing electricity in remote areas, fuel cells are transforming how we think about energy use and sustainability.
Whether you’re a student curious about green technologies, an engineer exploring alternatives to fossil fuels, or a policymaker seeking foundational knowledge, this course offers a deep dive into how fuel cells work, their real-world applications, the challenges they face, and the breakthroughs that could define our energy future. By the end, you’ll not only understand the science behind fuel cells but also the transformative role they can play in shaping a cleaner and more sustainable world.
Course Content
Introduction
Definition of fuel cell technology
00:00Brief history of fuel cell technology
00:00Importance of fuel cell technology in today’s world
00:00