Nature-Inspired Solutions: Biomimetic Engineering for Sustainable Innovation
Course Content
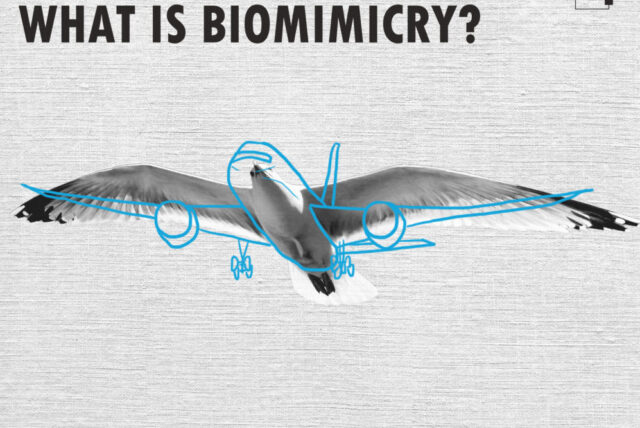
Introduction
-
Definition of biomimetic engineering
00:00 -
Importance of biomimetic engineering in achieving sustainable innovation
00:00 -
Overview of the book
00:00