Smart Grids: The Future of Energy Distribution and Management
About Course
As the global demand for electricity grows and climate concerns escalate, the need for intelligent, adaptive, and sustainable energy solutions has never been greater. Enter Smart Grids—the revolutionary leap in energy infrastructure that combines digital communication, automation, and cutting-edge analytics to create a more responsive and resilient grid. This course dives into the core of how smart grids operate, why they’re essential, and how they’re set to transform everything from how we consume electricity to how we integrate renewable energy into our homes and cities.
In this engaging course, students will explore the current challenges of traditional energy grids and how smart grids offer groundbreaking solutions for reliability, sustainability, and efficiency. Through real-world examples, interactive insights, and global case studies, you’ll gain a deep understanding of the technology, policy frameworks, and future possibilities driving the energy transition. Whether you’re an energy enthusiast, policymaker, or tech student, this course will energize your perspective on the electrified world of tomorrow.
Course Content
Introduction
Energy Security Threats
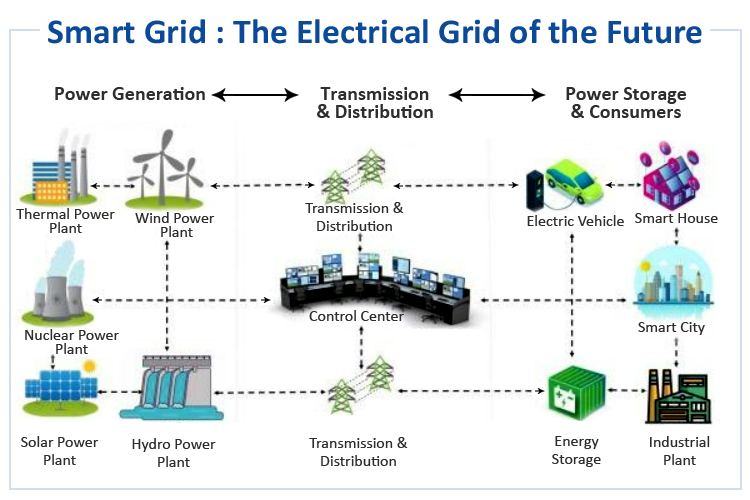
00:00Explanation of the concept of smart grids
00:00Why smart grids are important for the future of energy distribution and management
00:00Overview of what this eBook on smart grid will cover
00:00