The Internet of Things and Agriculture: A Revolution in Farming
Course Content
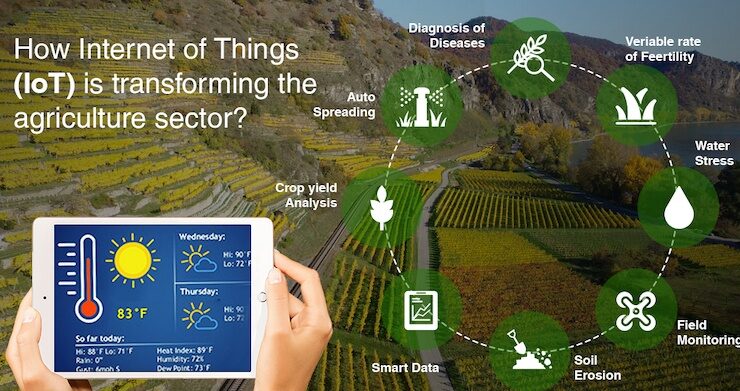
Introduction
-
Definition and overview of the Internet of Things (IoT)
00:00 -
Importance of IoT in agriculture
00:00 -
Purpose and scope of the eBook
00:00