The Power of Personalized Medicine: Harnessing Data to Improve Healthcare Outcomes
About Course
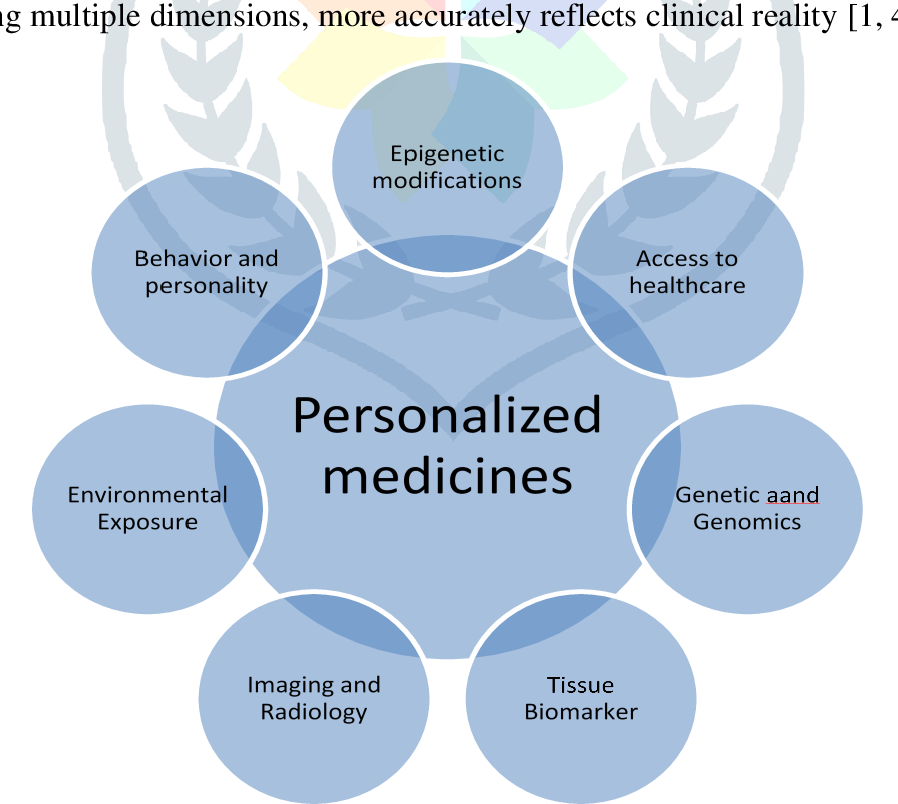
Imagine a world where your medical treatment is tailored not just to your disease, but to your DNA, environment, and lifestyle. Welcome to the transformative realm of Personalized Medicine, where the future of healthcare is precise, predictive, and profoundly personal. This course invites students to explore how cutting-edge technologies—like genomics, bioinformatics, and AI—are reshaping the way we understand and treat illness.
From decoding your genome to delivering targeted therapies, personalized medicine represents a seismic shift from a one-size-fits-all approach to individualized care. Through real-world examples, interactive case studies, and insights from current research, students will uncover how big data and molecular science converge to improve patient outcomes, reduce side effects, and revolutionize diagnostics and prevention. Whether you’re an aspiring healthcare professional, a data enthusiast, or simply curious about the future of medicine, this course will empower you to be part of the next healthcare revolution.
Course Content
Introduction
Definition of personalized medicine
00:00Historical background
00:00Why personalized medicine matters
00:00