Unlocking the Future: A Comprehensive Guide to Industry 4.0 Technologies
Course Content
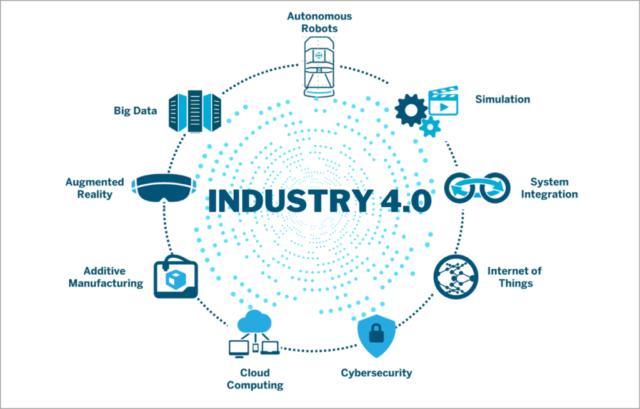
Introduction to Industry 4.0
-
The significance of Industry 4.0 in shaping the future of industries
00:00 -
Understanding the core principles and pillars of Industry 4.0
00:00 -
The transformative potential of Industry 4.0 technologies
00:00